DHCP Relay Option 82 Explained and Use Cases
The DHCP Relay Server ID Override and Link Selection Option 82 Suboptions feature enables the relay agent to be part of all Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) message exchanges by supporting the use of two suboptions of the relay agent information option (option 82). This design allows DHCPv4 to operate in networks where direct communication between the client and server is not possible or desired. These two suboptions used together enable the deployment of an architecture where having all DHCP traffic flow through the relay agent is desirable, allowing for greater control of DHCP communications.
This feature also introduces the capability to manually configure the interface for the relay agent to use as the source IP address for messages relayed to the DHCP server. This configuration allows the network administrator to specify a stable, hardware-independent IP address (such as a loopback interface).
Server ID Override Suboption
The server identifier (ID) override suboption allows the DHCP relay agent to specify a new value for the server ID option, which is inserted by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server in the reply packet. This suboption allows the DHCP relay agent to act as the actual DHCP server such that the renew requests will come to the relay agent rather than the DHCP server directly. The server ID override suboption contains the incoming interface IP address, which is the IP address on the relay agent that is accessible from the client. The DHCP client uses this information to send all renew and release request packets to the relay agent. The relay agent adds all of the appropriate suboptions and then forwards the renew and release request packets to the original DHCP server.
Link Selection Suboption
The link selection suboption provides a mechanism to separate the subnet/link on which the DHCP client resides from the the gateway address (giaddr), which can be used to communicate with the relay agent by the DHCP server. The relay agent will set the suboption to the correct subscriber subnet and the DHCP server will use that value to assign an IP address rather than the giaddr value. The relay agent will set the giaddr to its own IP address so that DHCP messages are routable over the network.
DHCP Relay Agent and DHCP Server Processing of Option 82 Suboptions
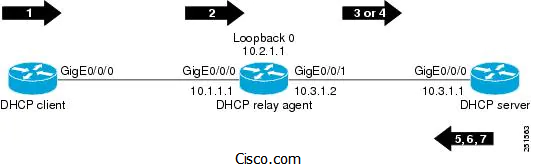
- The DHCP client generates a DHCP request and broadcasts it on the network.
- The DHCP relay agent intercepts the broadcast DHCP request packet and inserts a server ID override suboption and link selection suboption to its relay agent information option in the DHCP packet. The server ID override and link selection suboptions contain the incoming interface IP address, which is the IP address on the relay agent that is accessible from the client (10.1.1.1 in this case).
- The relay agent sets the gateway IP address (giaddr) to the IP address of an interface that is reachable by the DHCP server (typically the server-facing interface that will be used to transmit the message, 10.3.1.2 in this case).
- If the source interface is explicitly configured on a loopback interface (using the ip dhcp-relay source-interface command), the relay agent will use that address as the source IP address (giaddr) for messages relayed to the DHCP server (10.2.1.1 in this case).
The following processing occurs on the DHCP server after receiving the forwarded packets from the relay agent:
- The DHCP server uses the link selection suboption to locate the correct address pools for the DHCP client.
- The DHCP server sets the server ID option to the value specified by the server ID override suboption of the DHCP packet.
- The DHCP server sends the reply message to the IP address specified in the giaddr.
The DHCP client will see the relay agent address as the server ID and use that address when unicasting RENEW messages.
Example of use case is ACI DHCP relay:

![Explore The BGP Path Selection Attributes [Explained with Labs]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/image-28-800x450.png)