BGP MED Configuration Step by Step [Gns3 Lab]
![BGP MED Configuration Step by Step [Gns3 Lab]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/word-image-125.png?v=1647900714)
Contents
MED Overview
The Multi Exit Discriminator (MED) provides a dynamic way to influence another autonomous system (AS) in the way to reach a certain route when there are multiple entry points for that AS.
MED is propagated to all routers within the neighbor AS but not proapagated to other AS.
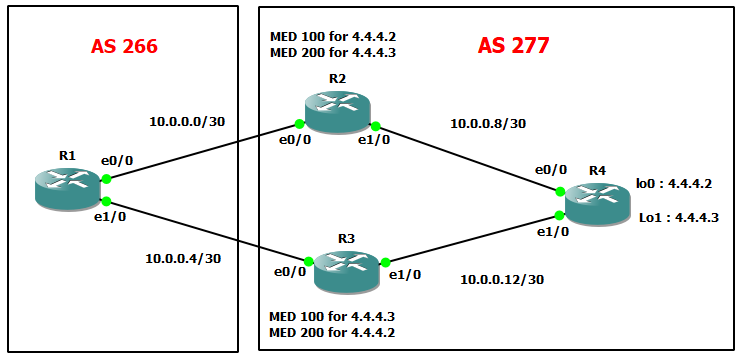
Topology
We will examine a topology where AS 266 have 2 entries to AS 277 and we want to manipulate preference for a prefix (out via neighbor R2) and another prefix via R3.
As we mentioned, MED is propagate inside AS 277, but will not be passed to other AS (if exist).
Initial configuration without MED Manipulation
* R1 Configuration:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router bgp 266
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.252
network 10.0.0.4 mask 255.255.255.252
neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 277
neighbor 10.0.0.6 remote-as 277
no auto-summary
* R2 Configuration:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.0.0.9 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
router bgp 277
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 266
neighbor 10.0.0.10 remote-as 277
no auto-summary* R3 Configuration:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.6 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.0.0.13 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router bgp 277
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.0.0.5 remote-as 266
neighbor 10.0.0.5 route-map MEDI out
neighbor 10.0.0.14 remote-as 277
no auto-summary
* R4 Configuration:
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 4.4.4.3 255.255.255.255
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.0.0.14 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router bgp 277
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 4.4.4.2 mask 255.255.255.255
network 4.4.4.3 mask 255.255.255.255
neighbor 10.0.0.9 remote-as 277
neighbor 10.0.0.13 remote-as 277
no auto-summary
Verifications:
So, before modifying the MED value, we can see that the subnets 4.4.4.2 and 4.4.4.3 are preferred via 10.0.0.2 which is the Router R2.
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 22, local router ID is 10.0.0.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 4.4.4.2/32 10.0.0.6 0 277 i
*> 10.0.0.2 0 277 i
* 4.4.4.3/32 10.0.0.6 0 277 i
*> 10.0.0.2 0 277 i
* 10.0.0.0/30 10.0.0.2 0 0 277 ?
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 10.0.0.4/30 10.0.0.6 0 0 277 ?
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.0.0.8/30 10.0.0.2 0 0 277 ?
*> 10.0.0.12/30 10.0.0.6 0 0 277 ?
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 2 subnets
B 4.4.4.2 [20/0] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:45
B 4.4.4.3 [20/0] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:45
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 4 subnets
B 10.0.0.8 [20/0] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:45
B 10.0.0.12 [20/0] via 10.0.0.6, 00:00:25
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
R1#Our target in the next part is to modify the MED value in order to:
- make the Endpoint 4.4.4.2 prefered via Router R2, to do this we will configure R2 to advertise this subnet to R1 with a lower metric (MED value) than the metric advertised by R3.
- make the Endpoint 4.4.4.3 prefered via Router R3, to do this we will configure R3 to advertise the subnet to R1 with a lower metric (MED value) than the metric advertised by R2.
MED Configuration
Let’s configure BGP and change the MED for each destination:
In Router R2: We will prefer route 4.4.4.2 by giving it a lower BGP metric (MED):
- we will set the MED value to 100 for 4.4.4.2 IP when advertising this route to R1.
- we will set the MED value to 200 for 4.4.4.3 IP when advertising this route to R1.
In Router R3: We will do the exact opposite in order to prefer route 4.4.4.3 by giving it a lower BGP metric (MED):
- we will set the MED value to 100 for 4.4.4.3 IP when advertising this route to R1.
- we will set the MED value to 200 for 4.4.4.2 IP when advertising this route to R1.
* R2 configuration:
We will prefer the 4.4.4.2 to pass through R2 by giving it a lower metric (100) and 4.4.4.3 a higher metric (200).
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.0.0.9 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
router bgp 277
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 266
neighbor 10.0.0.1 route-map MEDI out
neighbor 10.0.0.10 remote-as 277
no auto-summary
access-list 1 permit 4.4.4.2
access-list 2 permit 4.4.4.3
!
route-map MEDI permit 10
match ip address 1
set metric 100
!
route-map MEDI permit 20
match ip address 2
set metric 200
* R3 configuration:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.6 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.0.0.13 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router bgp 277
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.0.0.5 remote-as 266
neighbor 10.0.0.5 route-map MEDI out
neighbor 10.0.0.14 remote-as 277
no auto-summary
!
access-list 1 permit 4.4.4.2
access-list 2 permit 4.4.4.3
!
route-map MEDI permit 10
match ip address 1
set metric 200
!
route-map MEDI permit 20
match ip address 2
set metric 100
Verification:
After applying the MED manipulation (outbound), we can verify on R1 that:
- 4.4.4.2 (with Metric 100) preferred over R2
- 4.4.4.3 (with Metric 100) preferred over R3
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 2 subnets
B 4.4.4.2 [20/100] via 10.0.0.2, 00:01:32
B 4.4.4.3 [20/100] via 10.0.0.6, 00:01:21
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 35, local router ID is 10.0.0.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 4.4.4.2/32 10.0.0.6 200 0 277 i
*> 10.0.0.2 100 0 277 i
*> 4.4.4.3/32 10.0.0.6 100 0 277 i
* 10.0.0.2 200 0 277 i
*> 10.0.0.0/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.0.0.4/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R1#
![Explore The BGP Path Selection Attributes [Explained with Labs]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/image-28-800x450.png)