Storage concepts NAS, DAS & SAN Explained

Before diving into Storage types, let’s make some terms clear:
- Block level storage
- File level storage
Block Level storage:
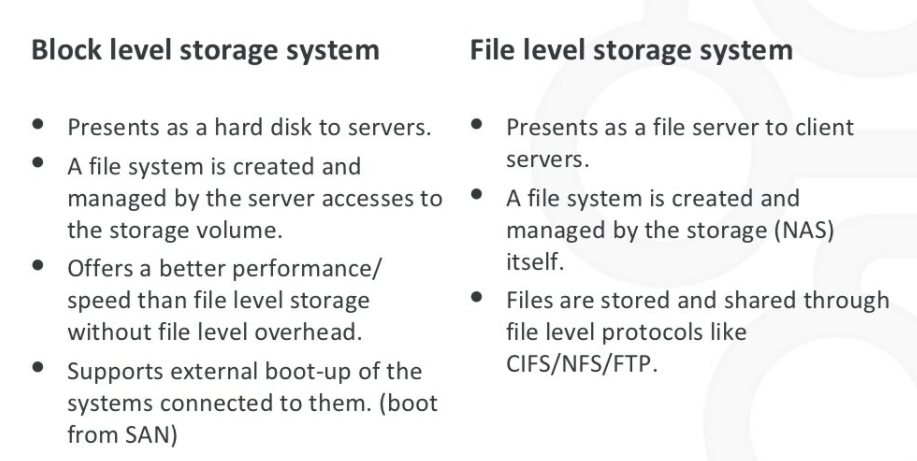
Block storage uses blocks, which are a set sequence of bytes, to store structured workloads. Each block is assigned a unique hash value which functions as an address. In block storage, the data is stored without any metadata e.g. data format, type, ownership, etc.
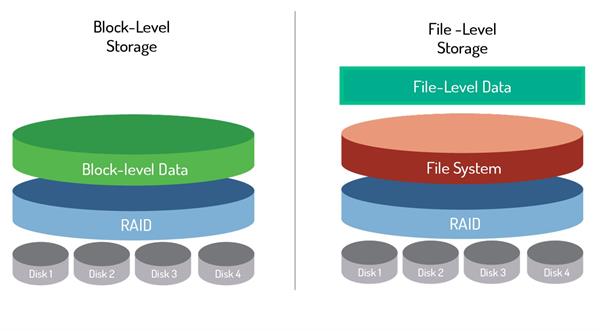
In block-level storage, a storage device such as a hard disk drive (HDD) is identified as something called a storage volume. A storage volume can be treated as an individual drive, a “block”. This gives a server’s operating system the ability to have access to the raw storage sections. The storage blocks can be modified by an administrator, adding more capacity when necessary, which makes block storage fast, flexible, and reliable.
The ability to store data in blocks delivers structured workloads such as databases, applications, etc. the freedom to decide how blocks are accessed, combined, or modified. Consequently, this makes block storage faster than other storage.
File Level storage:
File level storage, or file storage, is storage used for unstructured data and is commonly deployed in Network Attached Storage (NAS) systems. It uses Network File System (NFS) for Linux, and Common Internet File System (CIFS) or Server Message Block (SMB) protocols for Windows.
File level storage devices are often used to share files with users. By creating a block-based volume and then installing an operating system and attaching to that volume, you can share files out using that native operating system. Remember, when you use a block-based volume, you’re basically using a blank hard drive with which you can do anything.
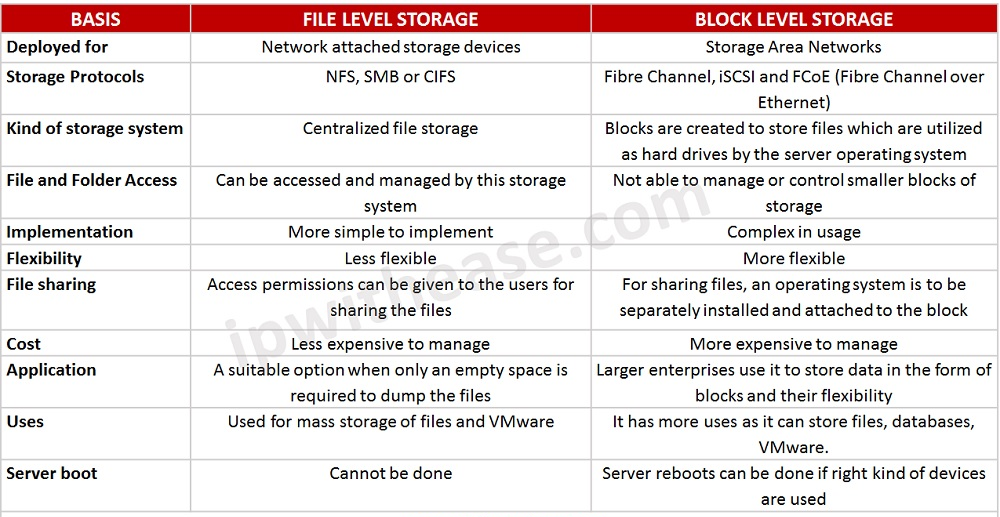
Block Level storage vs File Level storage:
File storage, as opposed to block storage, stores data in a hierarchical architecture; as such that the data and its metadata are stored as is – in the form of files and folders. Consequently, the stored data appears in a similar fashion to both systems; the one writing it and the one reading it.
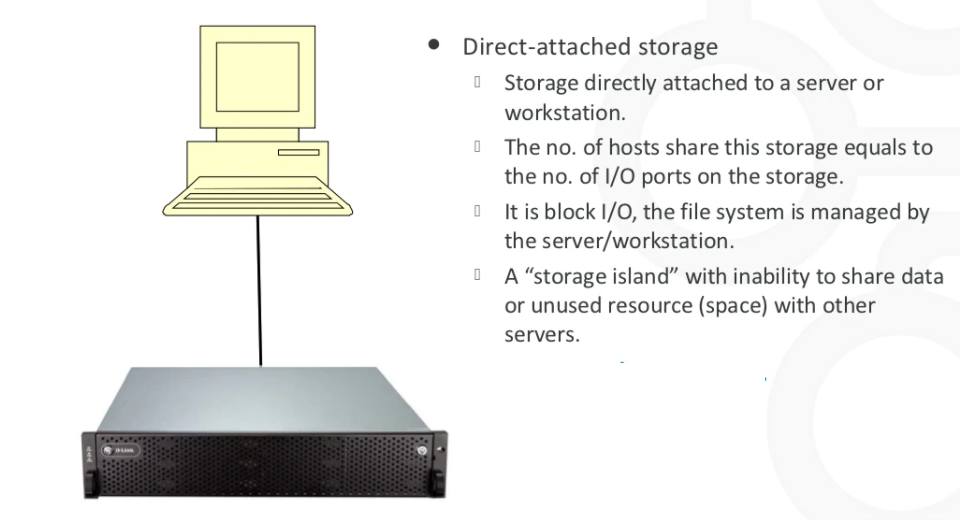
I- DAS: Direct-Attached Storage
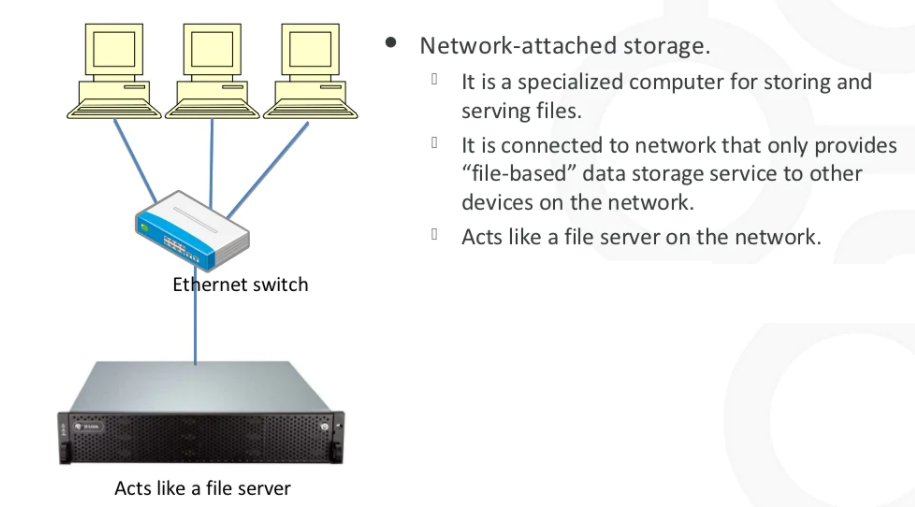
II- NAS: Network Attached Storage
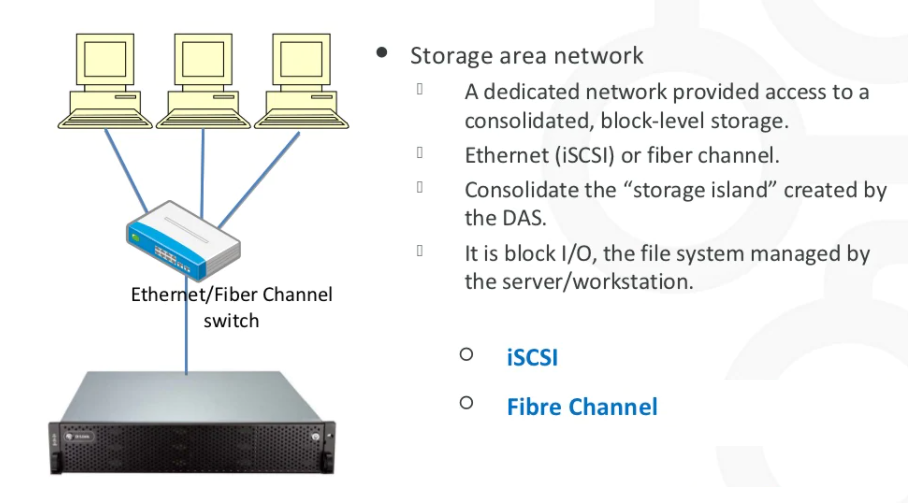
III- SAN: Storage Area Network
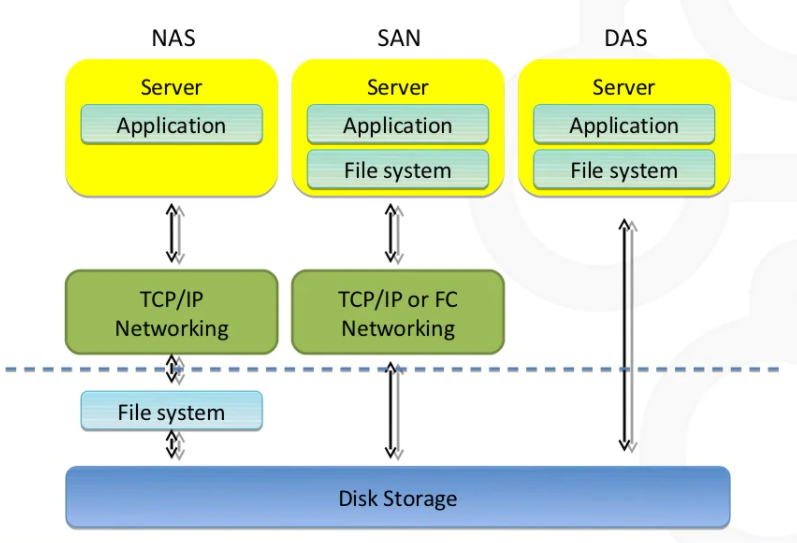
NAS vs SAN vs DAS:
Reference:
- slideshare.net/qsantechnology/what-is-storage-from-qsan-technology
- tutorialslink.com/Articles/What-is-File-Level-and-Block-Level-Storage-in-Virtualization-Concepts/2447
- stonefly.com/resources/what-is-file-level-storage-vs-block-level-storage/


![OSPF DR and BDR Election Explained [with Configuration]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-33.png?v=1647900046)
![OSPF Neighbor Adjacency Requirements [With Configuration]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-23-418x450.png?v=1647900064)
![OSPF Neighbor States Explained [Step by Step]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-13.png?v=1647900076)
![OSPF Area Types Explained and Configuration [Demystified]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-8.png?v=1647900083)