NSAP addressing and IS-IS NET Explained
NSAP Addressing
A Network Service Access Point address (NSAP address), defined in ISO/IEC 8348, is an identifying label for a service access point (SAP) used in OSI networking.
Network Service Access Point (NSAP) address aka ISO address is the network-layer address for CLNS packets (Connectionless Network Service).
For analogy with IP world:
- NSAP addressing can be compared to IP addressing
- CLNS can be compared to IP protocol.
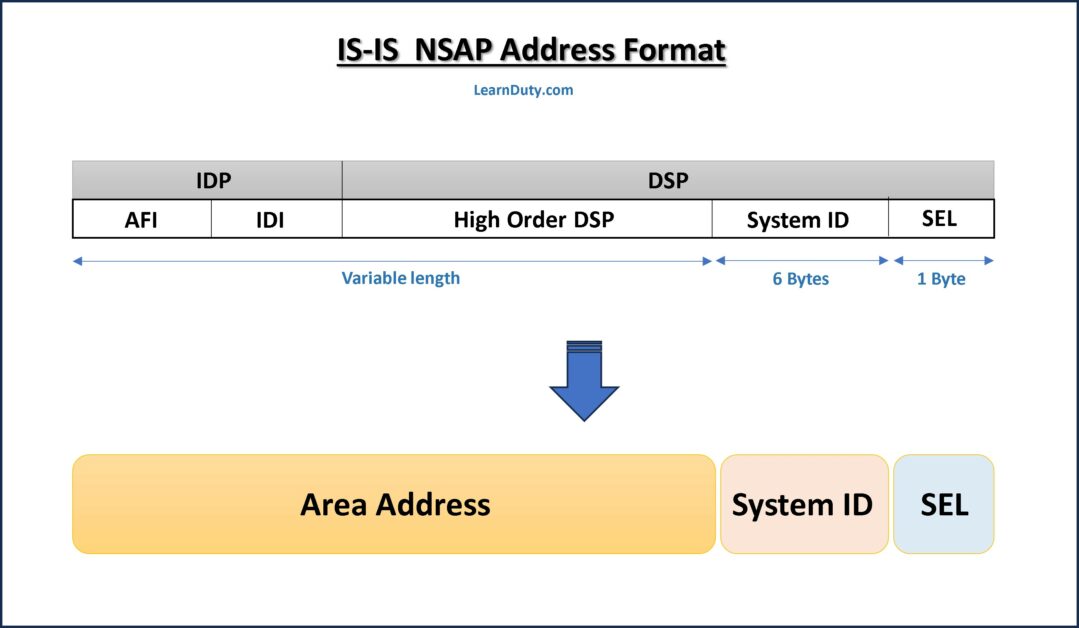
NSAP address composed of the Initial Domain Part (IDP) and the Domain Specific Part (DSP).
- The IDP refer to to the network ID of an IP address
- DSP refer to the subnet and host ID.
The IDP include:
- AFI – Authority and Format Identifier (1-byte): The AFI has a binary value between 0 and 99:
AFI specifies the organization authorized to assign addresses, and the format and length of the rest of the CLNP address. The AFI is always 8 bits.
AFI value identifies the IDI and DSP format. AFI set to 49 indicates private address space.
- IDI– Initial Domain Identifier (variable length): identifies the “suborganization” or sub-domain under the parent AFI organization. The length of the IDI is dependent on the AFI.
Note
The AFI plus the IDI essentially identify the “Autonomous System” of the address. However, this is not the equivalent of a BGP AS number
The DSP Include:
- HO-DSP (High-Order of DSP), it’s be used to identify the Area.
- System ID (System Identifier) (6-bytes), Identifies the host, it can contain the MAC address of the host.
- SEL (NSAP Selector) (1-byte), Identifies the type of service, for router it’s always 00
The combination of [IDP, HO-DSP] identify both the routing domain and the area within the routing domain. Hence the combination [IDP, HO-DSP] is called the “Area Address“. All nodes within the area must have same Area address.
IS-IS NET and System ID
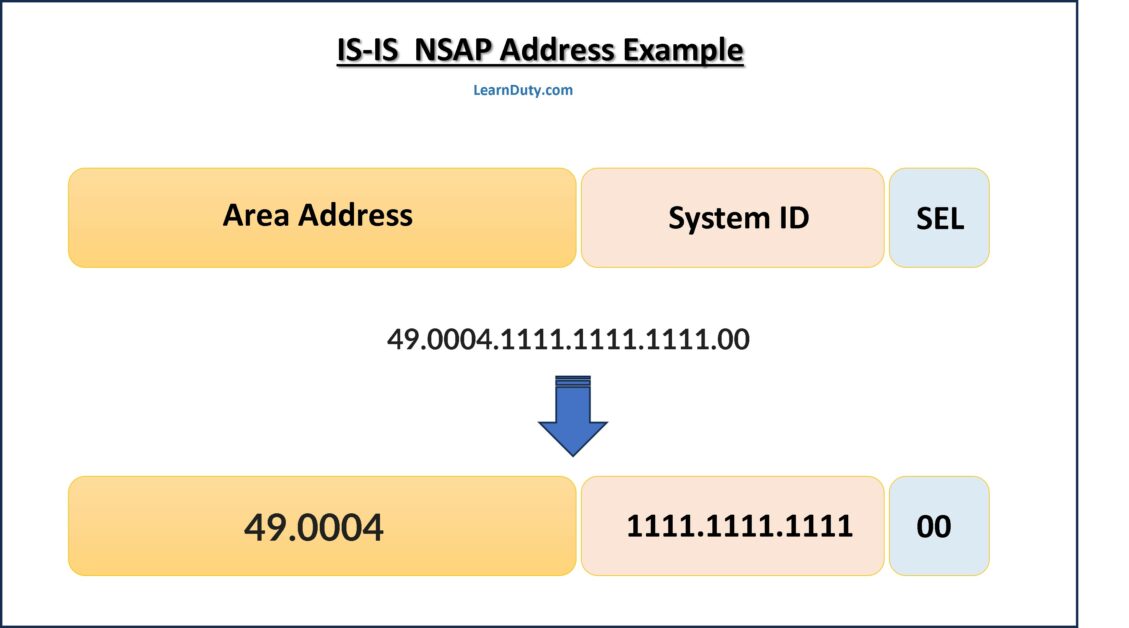
A Network Entity Title (NET) is an NSAP address with NSEL set to 0. The NSAP address for all routers (ISes) are set with NSEL equal to 0.
Each IS-IS instance has an associated network entity title (NET). The NET is comprised of the IS-IS system ID, which uniquely identifies this IS-IS instance in the area and the area ID.
For example, if the NET is 49.0004.1111.1111.1111.00:
- The area is ID 49.0004
- The system ID is 1111.1111.1111
- NSEL: 00
Please refer to this article for IS-IS protocol basics:
Reference:

![Explore The BGP Path Selection Attributes [Explained with Labs]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/image-28-800x450.png)