Understanding MAC Pinning [Cisco ACI Use Case Explained]
What is MAC Pinning
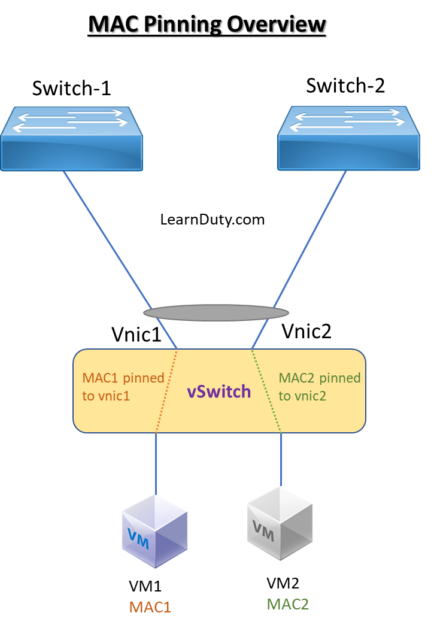
MAC pinning is used for pinning VM traffic in a round-robin fashion to each uplink based on the MAC address of the VM. This way, we can ensure that the MAC address of a virtual machine is never seen on multiple interfaces on the upstream switches, therefore, no flaps will occur.
vPC with LACP vs vPC with MAC Pinning:
- In a normal virtual port channel (vPC), a hash algorithm uses the source and destination MAC address to determine which uplink will carry a packet.
- In a vPC with MAC pinning, VM1 might be pinned to the first uplink, VM2 pinned to the second uplink, and so on.
- MAC pinning divides the uplinks from your server into standalone links and pins the MAC addresses to those links in a round-robin method. The drawback is that you cannot leverage the load sharing performance that LACP provides.
MAC pinning is the recommended option for channeling when connecting to upstream switches that do not support Multichassis EtherChannel (MEC).
MAC Pinning For AVS and AVE in Cisco ACI
In a MAC Pinning mode, the Gigabit Ethernet uplinks from the Cisco AVS or AVE are treated as stand-alone links. In a two Gigabit Ethernet uplinks scenario, each Gigabit Ethernet interface is connected to a separate physical switch with Layer 2 continuity on all IEEE 802.1Q trunked VLANs between the two switches.
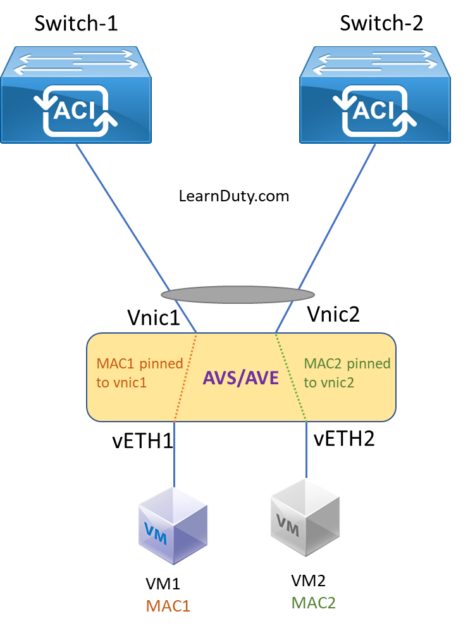
Virtual Ethernet ports supporting virtual machines and vmkernel ports are allocated in a round-robin fashion over the available Gigabit Ethernet uplinks. Each MAC address is pinned to one of the uplinks until a failover event occurs.
MAC pinning does not rely on any protocol to distinguish the different upstream switches, making the deployment independent of any hardware or design. This independence enables consistent and easy deployment of the Cisco AVS, and it is the preferred method for deploying the Cisco AVS or AVE when the upstream switches cannot be clustered using Cisco vPC.
MAC Pinning Use case in Cisco ACI AVE:
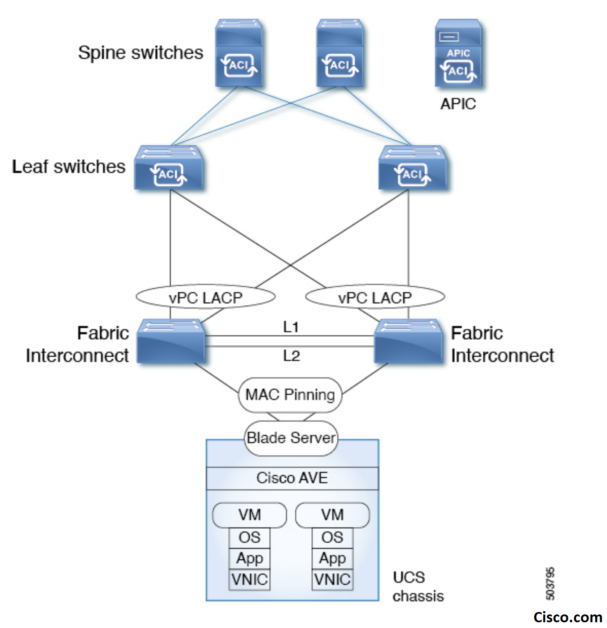
- The following picture from the ACI AVE Supported topologies document is an illustration of the use case where MAC Pinning is recommended:
- In this topology, the Cisco ACI Virtual Edge can be configured only with MAC pinning. That is because Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects don’t support LACP on the southbound ports towards the blade server. Therefore, the illustration shows MAC pinning only on the Cisco ACI Virtual Edge side. Each UCS Fabric Interconnect has a vPC Port-Channel to the same pair of leafs in a vPC Domain.
Consider the following restrictions when configuring MAC pinning:
- When a Cisco Application Virtual Switch or Cisco ACI Virtual Edge is deployed behind a vPC with MAC pinning and a host is connected to two leaf switches using that same vPC, reloading one of the two leaf switches can result in a few minutes of traffic disruption.
References:
- https://Cisco.com
- https://community.cisco.com