MPLS LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) Explained
What is LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) enables peer label switch routers (LSRs) in an MPLS network to exchange label binding information for supporting hop-by-hop forwarding in an MPLS network.
Ref: Cisco
The Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is a protocol defined by the IETF (RFC 5036) for the purpose of distributing labels in an MPLS environment.
Two routers with an established session are called LDP peers and the exchange of label mapping information is bi-directional. LDP is used to build and maintain LSP databases that are used to forward traffic through MPLS networks.
LDP uses reliable TCP as the transport protocol.
Abilities to set up LSPs dynamically based on routing information
LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) Process
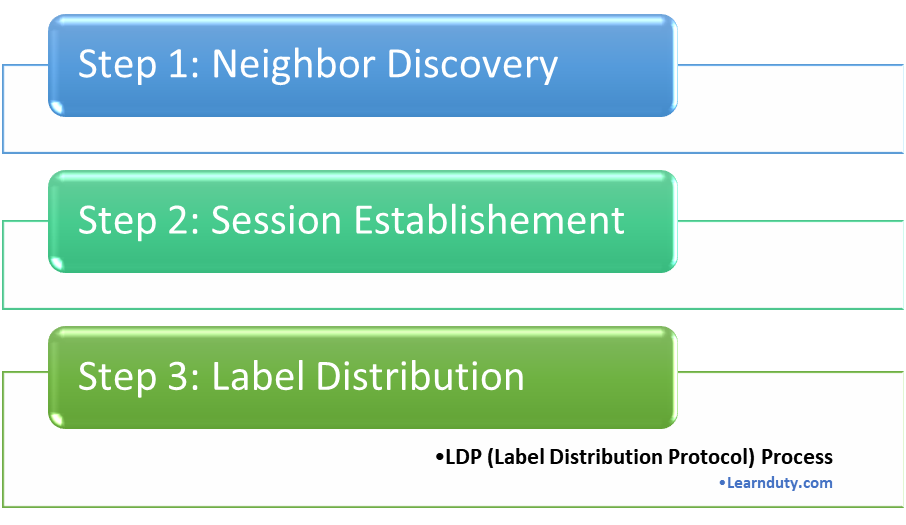
LDP Neighbor Discovery
LDP Neighbor Discovery is achieved via LDP Hello messages.
LDP Hello messages use UDP as transport layer protocol. These messages are sent on the link to the multicast IP address: 224.0.0.2 which is called “All Routers on this Subnet”.
The UDP port used for LDP is 646.
Each MPLS Capable Router (LSR) will send an UDP Packet containing LDP Hello to the All Routers on this Subnet Multicast Address 224.0.0.2 with Destination port 646.

![Explore The BGP Path Selection Attributes [Explained with Labs]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/image-28-800x450.png)