IGMP Explained & Basic Configuration on Nexus
What is IGMP:
IGMP is an IPv4 protocol that a host uses to request multicast data for a particular group. Using the information obtained through IGMP, the software maintains a list of multicast group or channel memberships on a per-interface basis. The systems that receive these IGMP packets send multicast data that they receive for requested groups or channels out the network segment of the known receivers.
By default, the IGMP process is running. You cannot enable IGMP manually on an interface. IGMP is automatically enabled when you perform one of the following configuration tasks on an interface:
- Enable PIM
- Statically bind a local multicast group
- Enable link-local group reports
IGMP Versions:
The device supports IGMPv2 and IGMPv3, and IGMPv1 report reception.
By default, the software enables IGMPv2 when it starts the IGMP process. You can enable IGMPv3 on interfaces where you want its capabilities.
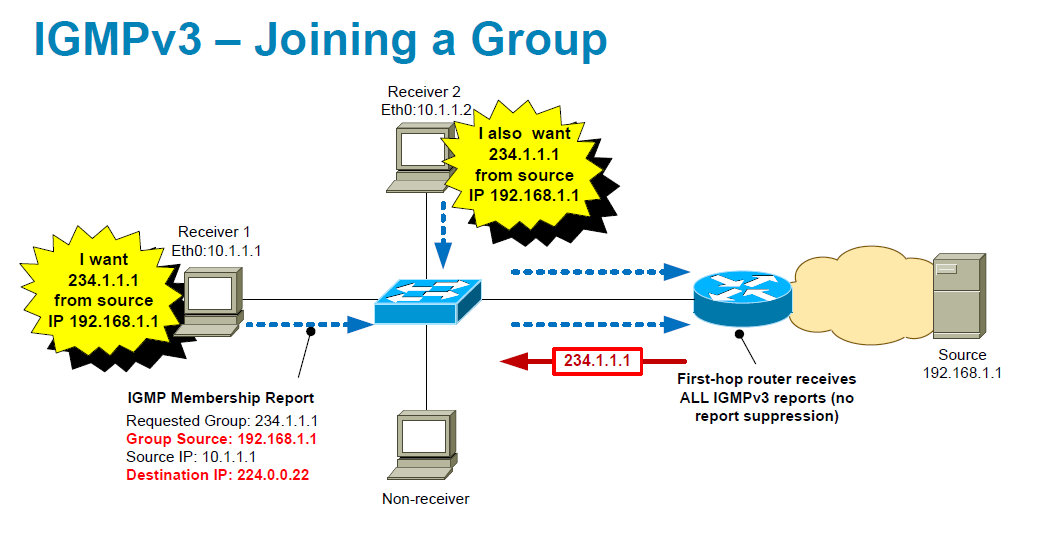
IGMPv3 includes the following key changes from IGMPv2:
- Support for Source-Specific Multicast (SSM), which builds shortest path trees from each receiver to the source, through the following features:
- Host messages that can specify both the group and the source.
- The multicast state that is maintained for groups and sources, not just for groups as in IGMPv2.
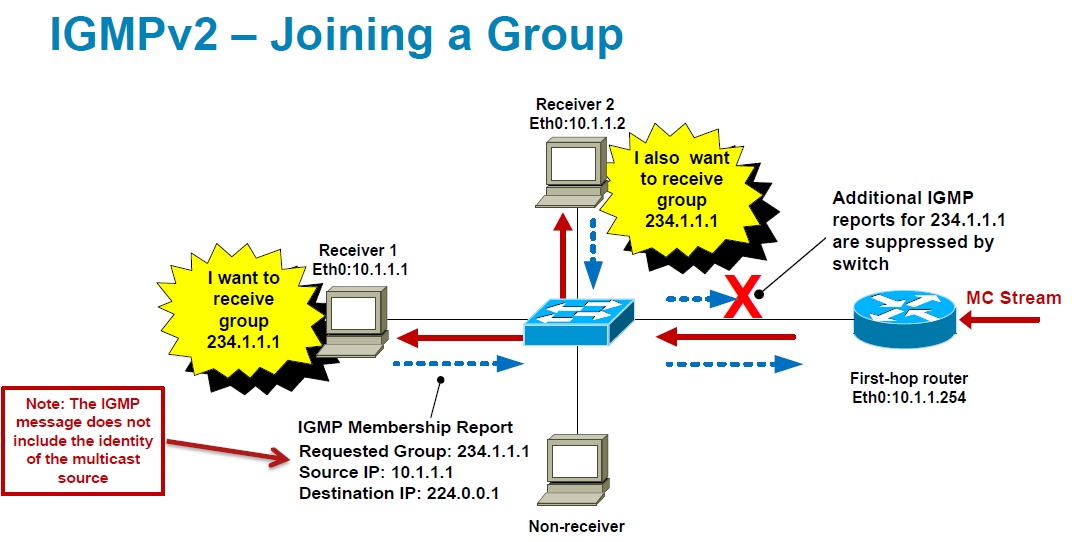
- Hosts no longer perform report suppression, which means that hosts always send IGMP membership reports when an IGMP query message is received.
IGMP Basics:
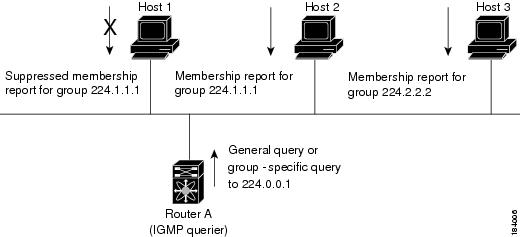
This figure shows the basic IGMP process of a router that discovers multicast hosts. Hosts 1, 2, and 3 send unsolicited IGMP membership report messages to initiate receiving multicast data for a group or channel.
In the figure below, router A, which is the IGMP designated querier on the subnet, sends query messages to the all-hosts multicast group at 224.0.0.1 periodically to discover whether any hosts want to receive multicast data. You can configure the group membership timeout value that the router uses to determine that no members of a group or source exist on the subnet.
The software elects a router as the IGMP querier on a subnet if it has the lowest IP address. As long as a router continues to receive query messages from a router with a lower IP address, it resets a timer that is based on its querier timeout value. If the querier timer of a router expires, it becomes the designated querier. If that router later receives a host query message from a router with a lower IP address, it drops its role as the designated querier and sets its querier timer again.
In this figure, host 1’s membership report is suppressed, and host 2 sends its membership report for group 224.1.1.1 first. Host 1 receives the report from host 2. Because only one membership report per group needs to be sent to the router, other hosts suppress their reports to reduce network traffic. Each host waits for a random time interval to avoid sending reports at the same time. You can configure the query maximum response time parameter to control the interval in which hosts randomize their responses.
IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 membership report suppression occur only on hosts that are connected to the same port.
IGMPv3 hosts do not perform IGMP membership report suppression:
Default IGMP Parameters:
| Parameters | Default |
|---|---|
| IGMP version | 2 |
| Startup query interval | 30 seconds |
| Startup query count | 2 |
| Robustness value | 2 |
| Querier timeout | 255 seconds |
| Query timeout | 255 seconds |
| Query max response time | 10 seconds |
| Query interval | 125 seconds |
| Last member query response interval | 1 second |
| Last member query count | 2 |
| Group membership timeout | 260 seconds |
| Report link local multicast groups | Disabled |
| Enforce router alert | Disabled |
| Immediate leave | Disabled |
IGMP Configuration on NX-OS:
Switch(config)# interface e1/10
Switch(config-if)# ip igmp version versionCode language: PHP (php)To verify the interfaces that are activated for IGMP, which version of IGMP is used, and the number of groups that the receivers have joined on that interface, use the show ip igmp interface brief command.
Related article: IGMP Snooping
References:
IGMP Basics
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus9000/sw/6-x/multicast/configuration/guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-OS_Multicast_Routing_Configuration_Guide/b_Cisco_Nexus_9000_Series_NX-OS_Multicast_Routing_Configuration_Guide_chapter_010.html


![OSPF DR and BDR Election Explained [with Configuration]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-33.png?v=1647900046)
![OSPF Neighbor Adjacency Requirements [With Configuration]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-23-418x450.png?v=1647900064)
![OSPF Neighbor States Explained [Step by Step]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-13.png?v=1647900076)
![OSPF Area Types Explained and Configuration [Demystified]](https://learnduty.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/image-8.png?v=1647900083)